Motherboard or mainboard what it is and what it is used for
The basic structure of every computer, the motherboard is the skeleton, the neural system and the power supply of each component. 
Usually a larger element than the computer itself, the motherboard or mainboard in English is a printed circuit (PCB) that acts as the basis for all the components.
Present in any electronic device, the motherboard performs several fundamental functions:
Probably the "oldest" electronic component of the PC, the motherboard has been constantly renewed, adapting to new hardware in order to make it perform at its best. In addition to adapting to new needs, the motherboard has also adapted dimensionally.
Motherboard Formats
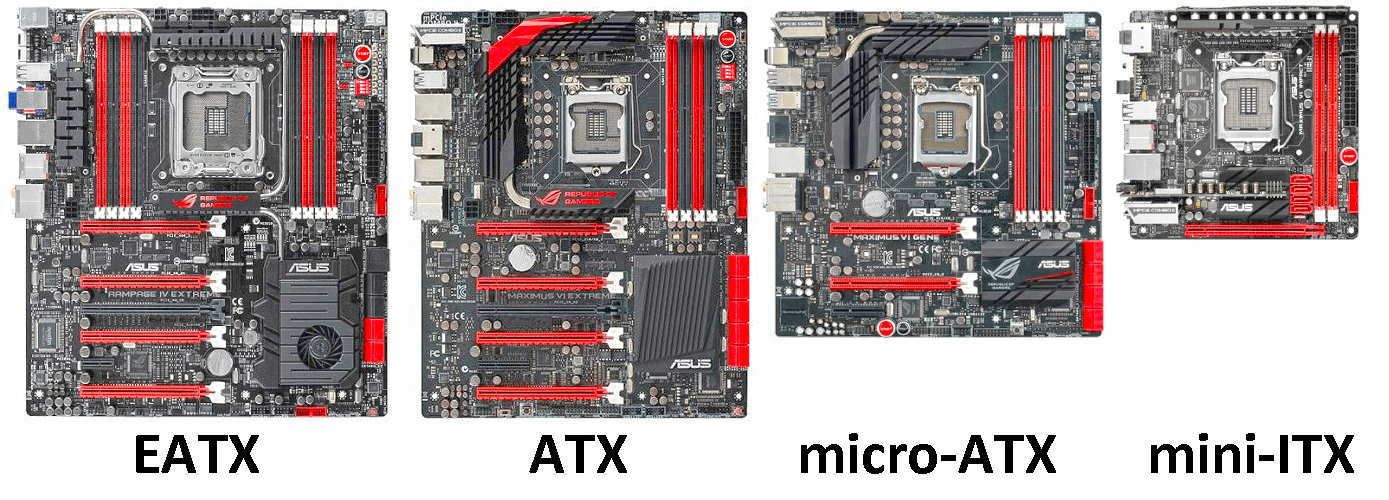
Obviously, the motherboard does not always have the same shape or size. In fact, we have some formats, in the computer sector, which we can consider as standards and which "reflect" what has already been indicated and proposed for cases.
In particular, the motherboard is usually available in three "sizes":
ATX format: created by Intel, born in 1995. The result of modifications, corrections and implementations over time, it has now reached a standard form that distinguishes it. Developed on a rectangle with dimensions equal to 305x244 millimetres, it hosts on its surfaces an enormous quantity of slots for RAM memory banks and many connectors for cards. The arrangement is designed to facilitate cooling of the components. This motherboard format is the most used, including almost all normal computers ; microATX format: format dedicated to compact computers. The main criterion in designing this format is size, so the available slots on this card have been limited. In fact, we find space for only two memory slots and very few additional cards. This card, which has a size of 243x205 millimeters, is designed for office computers, non-demanding PCs and without the need for complex cooling systems.In addition to these three standard formats, we also find special sizes, usually dedicated to professional PCs (graphic uses or video editing) or those designed as " gaming computers ".
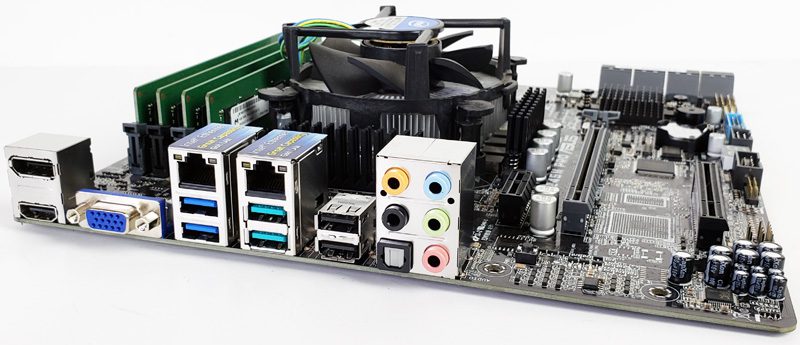
Components present on the motherboard
The main components of a motherboard are many and each performs a specific function. The function of this card is to support them "physically" and put them in communication with each other, allowing a continuous exchange of data between the hard disks, the RAM, the CPU and the other hardware parts present in the computer.
In fact, on this board we find printer circuits and electronic components (transistors, capacitors, etc.) as well as some standard components of the motherboard itself:
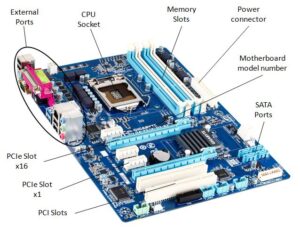 Chipsets
Chipsets
A fundamental component of the computer , the chipset is a set of components (Bridges) whose function is to organize and manage the flow of data between the various parts. The first component, the northbridge, acts as a connection between the processor and high-speed peripherals, such as RAM and the video controller. The other, technically known as the southbridge, connects the CPU to slower peripherals.
The chipset, the nerve center for the speed and stability of PC communications, is made by the CPU manufacturer. This is why when we go to choose a motherboard we already find the processor installed or at least a list of processors supported by that specific configuration
Sockets
Another component in which the CPU manufacturer is heavily involved is the socket. An actual CPU container, it houses the CPU itself, allowing safe attachment from a mechanical, electronic and power supply point of view to the motherboard .
The socket is nothing more than a plastic base firmly fixed on the motherboard. This base allows you to mount and dismount the CPU quickly and without risk of breakage or need for specific equipment.
Expansion slots
The concept of “cradle” is not used exclusively for the CPU . All hardware components that attach to the motherboard do so via "headers" or "sockets". Real alternative sockets that are normally referred to as expansion slots.
In modern PCs we find three different types of slots:
Auxiliary connectors
In addition to slots and sockets on the motherboard we find a wide range of connectors. Very large variety and number, given the total number of components that can and must be connected to the board. Among the main ones we find:
Power supply system
The motherboard also provides electrical power to the various components. The power supply, in fact, is responsible for converting the current from alternating to direct current and lowering the voltage, and then "bringing it" to the motherboard, which through various channels powers the CPU , the RAM memories, the hard disks and follow all other tabs and ports.
I/O panel
The motherboard is also equipped with an external interface. This panel, called I/O, is usually placed vertically on the back of the case. On the same we find the connections for standard devices and network communications. There are usually several USB ports, analogue connectors for mouse and keyboard, the network connector, the sound card connector and, depending on the type of PC, sometimes also the video card connector. The presence of a possible dedicated card can then allow you to have a double option (network cards) or exclude the connector on the motherboard (for example for audio and video cards).